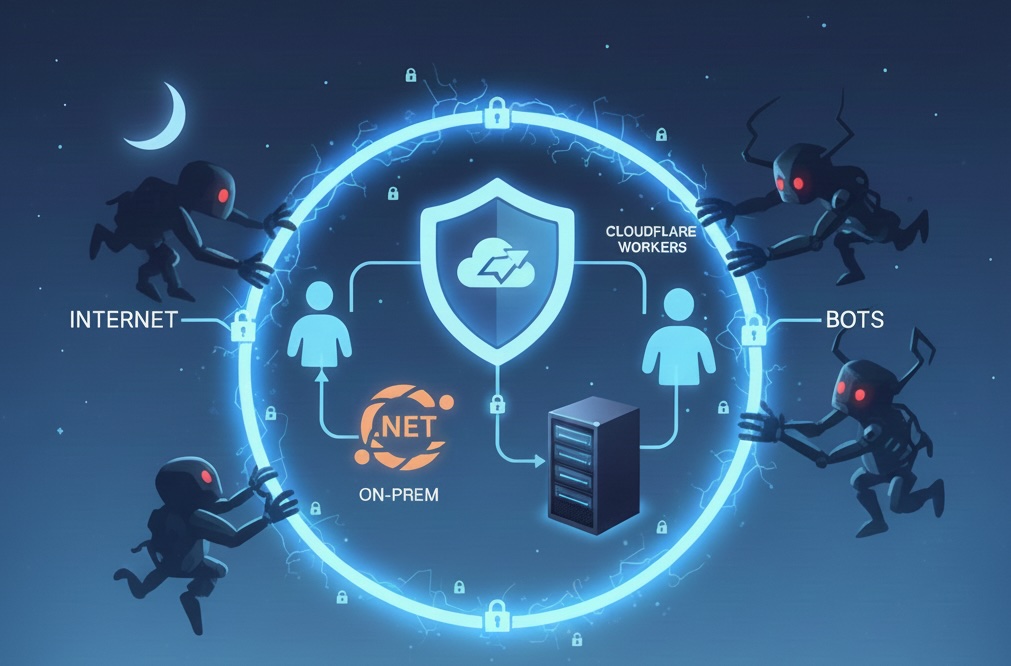
How do I use Cloudflare to safely self host a .NET application on prem and tunnel services safely to my on prem server, that my cloudflare workers can talk to, in a way that the internet and bots cannot access at all, so that I can sleep safely at night?
Disclaimer
This is part of my day 1 series that I am doing to push the limits of what I can achieve with onprem cheap servers, .NET and Cloudflare. This is not for production, and is purely for experimental study purposes. Each blog post (how to) will be published before I actually implement anything and will be followed up with a link to a reference architecture of anything I implement. i.e. Instructions below were generated by Gemini (the title of this post is the prompt); your results will vary and be different. All normal AI warnings apply, follow steps below at your own risk, not for production, do not swollow, do not eat these instructions, do not operate any heavy machinery or fly a commercial aeroplane with passengers whilst following any of these instructions ... kapich?
Also; the real value of these posts won't be the content that the AI spits out, anyone can do that, it will be the amendments and corrections I add after I test these steps myself. (i.e. human in the loop)
Overview (good luck!)
The solution is to use Cloudflare Tunnel (formerly Argo Tunnel) with Cloudflare Access to create a secure, outbound-only connection from your on-premises server to Cloudflare's network. This ensures:
No inbound ports need to be opened on your firewall
No public IP exposure - your server is invisible to the internet
Cloudflare Workers can communicate with your on-prem service via the tunnel
Zero Trust security - only authenticated/authorized requests reach your server
Architecture Components
1. Cloudflare Tunnel (cloudflared)
Cloudflare Tunnel creates an outbound-only connection from your on-prem server to Cloudflare's edge network. The tunnel:
Initiates connections FROM your server TO Cloudflare (outbound only)
No inbound firewall rules needed
Your server's IP is never exposed to the internet
Traffic is encrypted end-to-end
2. Cloudflare Access (Zero Trust)
Cloudflare Access provides authentication and authorization:
Only authenticated requests reach your tunnel
Can integrate with identity providers (OAuth, SAML, etc.)
Service tokens for machine-to-machine communication (Workers → Tunnel)
IP-based access rules if needed
3. Cloudflare Workers
Your Workers can communicate with the on-prem service via:
Service tokens for authentication
Private network routing through the tunnel
No public internet exposure
Implementation Steps
Step 1: Install cloudflared on Your On-Prem Server
Windows:
# Download and install cloudflared
# Or use Chocolatey: choco install cloudflaredLinux:
# Download latest release
wget https://github.com/cloudflare/cloudflared/releases/latest/download/cloudflared-linux-amd64
chmod +x cloudflared-linux-amd64
sudo mv cloudflared-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/cloudflaredmacOS:
brew install cloudflaredStep 2: Authenticate cloudflared
cloudflared tunnel loginThis opens a browser to authenticate with your Cloudflare account and grants the tunnel permission to create routes.
Step 3: Create a Tunnel
# Create a named tunnel
cloudflared tunnel create bookify-onprem
# This creates a tunnel and generates a UUID
# Save the tunnel UUID - you'll need it for configurationStep 4: Configure the Tunnel
Create a configuration file (e.g., config.yml):
tunnel: <your-tunnel-uuid>
credentials-file: /path/to/credentials.json
ingress:
# Route traffic to your .NET application
- hostname: api.yourdomain.com
service: http://localhost:5000 # Your .NET app's local address
# Catch-all rule (must be last)
- service: http_status:404Important: Your .NET application should bind to localhost or a private IP, NOT to 0.0.0.0 or a public interface.
Step 5: Configure Cloudflare Access (Zero Trust)
Go to Cloudflare Zero Trust Dashboard
Configure Application Settings:
Configure Access Policies:
Protect the Tunnel Route:
Step 6: Run the Tunnel
# Run the tunnel
cloudflared tunnel run bookify-onprem
# Or run with config file
cloudflared tunnel --config config.yml runFor Production (Windows Service):
# Install as Windows service
cloudflared service install
cloudflared service startFor Production (Linux Systemd):
# Create systemd service file: /etc/systemd/system/cloudflared.service
[Unit]
Description=Cloudflare Tunnel
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=cloudflared
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/cloudflared tunnel --config /etc/cloudflared/config.yml run
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5s
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
# Enable and start
sudo systemctl enable cloudflared
sudo systemctl start cloudflaredStep 7: Configure Your .NET Application
appsettings.json:
{
"Kestrel": {
"Endpoints": {
"Http": {
"Url": "http://localhost:5000"
}
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "api.yourdomain.com"
}Program.cs (minimal example):
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Only bind to localhost
builder.WebHost.UseUrls("http://localhost:5000");
// Add your services
builder.Services.AddControllers();
// ... other services
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure middleware
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();Step 8: Configure Cloudflare Workers to Access On-Prem Service
In your Cloudflare Worker, use the service token to authenticate:
export default {
async fetch(request, env) {
// Use service token for authentication
const response = await fetch('https://api.yourdomain.com/your-endpoint', {
headers: {
'CF-Access-Client-Id': env.CF_ACCESS_CLIENT_ID,
'CF-Access-Client-Secret': env.CF_ACCESS_CLIENT_SECRET,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
method: 'POST',Worker Environment Variables:
CF_ACCESS_CLIENT_ID: From your service tokenCF_ACCESS_CLIENT_SECRET: From your service token
Security Best Practices
1. Network Isolation
Never bind your .NET app to 0.0.0.0 - only localhost or private IPs
Use firewall rules to block all inbound traffic except from localhost
Consider running in a DMZ or isolated network segment
2. Cloudflare Access Policies
Use Service Tokens for machine-to-machine communication
Implement IP allowlisting if you know Cloudflare Worker IP ranges (optional, as Access handles this)
Set appropriate session durations
Enable audit logs to monitor access
3. Application Security
Use HTTPS within the tunnel (Cloudflare handles TLS termination)
Implement proper authentication/authorization in your .NET app
Use API keys or JWT tokens for additional security layers
Enable CORS properly (only allow your Cloudflare domain)
Implement rate limiting
4. Tunnel Security
Store credentials securely (use encrypted storage)
Use least-privilege service accounts
Monitor tunnel health and logs
Set up alerts for tunnel disconnections
Use separate tunnels for different environments (dev/staging/prod)
5. Monitoring and Logging
Enable Cloudflare Analytics to monitor traffic
Log all requests in your .NET application
Set up alerts for suspicious activity
Monitor tunnel uptime
Additional Considerations
Performance
Cloudflare Tunnel adds minimal latency (~10-50ms typically)
Consider using Cloudflare's private network routing for lower latency
Monitor bandwidth usage
High Availability
Run multiple tunnel instances for redundancy
Use Cloudflare's load balancing if needed
Implement health checks
Cost
Cloudflare Tunnel is free for basic usage
Cloudflare Access has free tier (50 users)
Consider Cloudflare Workers pricing for your use case
Alternative: Cloudflare Private Network
For even more security, consider using Cloudflare's Private Network feature, which creates a private network between your Workers and on-prem resources without any public internet exposure.
Verification Checklist
[ ] Tunnel is running and connected (check
cloudflared tunnel info)[ ] No inbound firewall rules are open
[ ] .NET app only binds to localhost
[ ] Cloudflare Access is configured and protecting the route
[ ] Service tokens are created and configured in Workers
[ ] Direct internet access to your server IP is blocked
[ ] Monitoring and alerting are set up
[ ] Logs are being collected and reviewed
Troubleshooting
Tunnel won't connect:
Check firewall allows outbound HTTPS (port 443) to Cloudflare
Verify credentials file is correct
Check tunnel UUID matches configuration
Workers can't reach on-prem service:
Verify service token is correctly configured
Check Access policies allow the service token
Verify the tunnel route is correct
Check .NET app is running and accessible on localhost
Access denied errors:
Verify Access policies are correctly configured
Check service token hasn't expired
Review Access logs in Zero Trust dashboard
Summary
This architecture provides: ✅ Zero inbound exposure - no ports open to internet ✅ Secure communication - encrypted end-to-end ✅ Access control - Zero Trust authentication ✅ Worker integration - Service tokens for machine-to-machine ✅ Peace of mind - Your server is invisible to bots and attackers
Your on-prem .NET application is now safely accessible only through Cloudflare's secure tunnel, with no direct internet exposure.
Updates and Corrections
Updates and corrections might go here, or I might try to squeeze them inline perhaps strikethrough and replacement with a highlighter, if they're minor. If it's a total cluster-***** I might just delete this whole post and rewrite the whole thing later, we'll see what day 2 brings. 😂